- By Shougat Dasgupta
- Artwork by Alveena Turi
My parents moved from Bombay to Kuwait when I was six weeks old. We moved because the money was good, the living was easy, and it had none of the grime of India, the clamorous crowds in the cities we left behind. Their kids, my parents told themselves, would have better opportunities in the Gulf. Not that any of us had it all that hard in India. But India was not Kuwait.
Then, when I was 12, hundreds of thousands of Iraqi soldiers, hardened by a ruinous, nearly decade-long war with Iran, annexed Kuwait.
The Big Idea: Age of nostalgia
Infatuation with a mythologized history has overtaken communities, cultures, entire regions, sending society and identity into a fun-house mirror of nostalgic reflections. This special issue brings you stories of people finding solace in pasts imagined and grieving for futures foreclosed in a time of existential threats.
Nostalgia has both been harnessed for political ends and become its own political force, electrifying powerful currents of populism, jingoism, and longing for dynastic rule. It also reaches deep into the crevices of human feeling — in kitchen table conversations and on TikTok alike — leading to a thickening of anger, loss, and sadness.
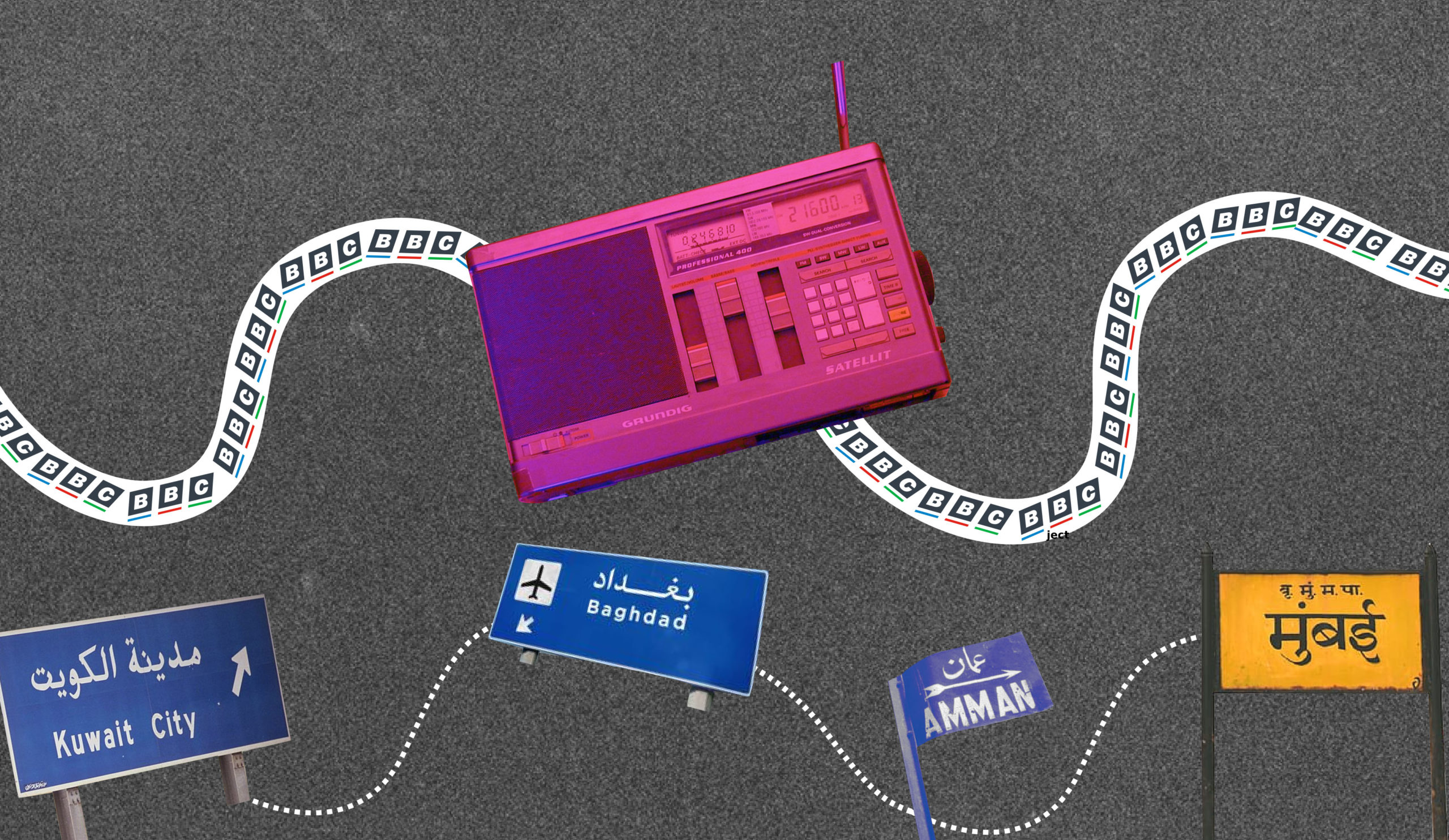
I slept through the invasion, waking to the sound of the news on my shortwave radio, which my father had commandeered. This radio — an industrial slate-gray Grundig Satellit 650, stolid, weighty and unglamorous, “just like German girls” as my Calcutta-born, Germany-educated father would say — was a major presence in my life.
This radio, or rather the hours I spent with my ear soldered to it, listening to the BBC World Service, was at fault for what my mother called my “Britification.” My Anglophilia had long made me the object of family scorn. Hobson-Jobson, or Suited-Booted, my dad would call me when he was feeling affectionate, “ingrej” (meaning Englishman, albeit spat contemptuously from the side of his mouth) when less so.
Football was where my devotion to all things English was most manifest. I lived then for Saturday evenings, coming home from school — the weekend in Kuwait was Thursday and Friday — to coax from the radio’s bleeps and crackles the poetry of the classified football results, the sounds of those long lists of British provincial centers and market towns.
For all the evocative power of England’s various Wanderers, Rovers and Rangers, it was the Scottish teams that were unmatched for euphony. Cowdenbeath, Stenhousemuir, Partick Thistle, Queen of the South and, most stirring of all to my seven-year-old ears, Heart of Midlothian. Only the Scottish league could have produced, though it never did, such a scoreline as East Fife 5 – Forfar 4. Read it out loud for yourself.
My experience of football was more vivid because it was untainted by television coverage. What mattered to me were the stories, the lore and the private pleasures of the imagination rather than the community solidarity of following one’s local football club.
“Listen,” my father said, retaining, in the midst of crisis, the paternal imperative to needle his son, “it’s your prime minister.” Margaret Thatcher was denouncing the Iraqi invasion as “absolutely unacceptable,” her peremptory tone typical of the more fearsome teachers in my British school.
My father thought the whole thing would blow over. “Bush and Thatcher won’t allow it. Saddam will pull out within a week,” my parents told me and my sister, told their friends, told our relatives around the world, told each other. After all, the previous day’s Arab Times, the bigger of Kuwait’s two English-language dailies, had announced on its front page that the problem “between brothers” had been settled. And then the Iraqis cut the phone lines.

In 1990, globalization was an idea gaining currency in academic circles. As cosmopolitan pre-teens, defined not so much by where we came from as by what we read, watched, heard and thought, you could say my friends and I anticipated the zeitgeist. So in that tiny, undistinguished country in the Arabian Gulf, I drank the British fruit cordial Vimto and ate Hardee’s roast beef sandwiches. I spread Danish butter on my toast and only ate Granny Smith apples. I loved “The Real Genius,” starring Val Kilmer, and also loved the movies of Satyajit Ray that I watched with my parents. I supported Liverpool Football Club. I listened to New Order and The Smiths and Gang of Four and Orange Juice. On my bookshelves, Tintin and Asterix comics shared space with Archie digests and Amar Chitra Katha.
Such scattershot particulars, such quirks of personality, I understood. “Indian,” “Bengali,” I did not. My migrant parents — though migration is surely the ultimate expression of the individual over the community, over the ties that bind — still sought succor in a collective identity, in their sense of themselves as part of a community.
When my father joked that Margaret Thatcher was my prime minister, he knew that Thatcher, the leader of a country to which I had no ties that any immigration officer would recognize, might as well have been my prime minister, just as George H.W. Bush might as well have been my president, or Sheikh Jaber al-Ahmad al-Jaber al-Sabah my emir, because I did not know what it meant to have such allegiances.
What he didn’t seem to know was that my Anglophilia was a result of moving to Kuwait, of flailing for identity in a country to which I could never belong. Identity, I knew from an early age, was nebulous, its edges as unruly as an ink stain.
India offered me my external identity, Britain my interior one and Kuwait was the metaphorical suburban bedroom in which I played out my fantasies. For our family, Kuwait wasn’t as final as emigration. It elicited no real grief, no loss. Even if it lasted years, decades, it was a temporary condition. Home was elsewhere.

Before the invasion, an exasperated teacher once accused me of daydreaming with the words: “You really do live in your own utopia.”
Looking the word up in the dictionary that night, I discovered that utopia meant “no place.” It occurred to me that I might be living in Utopia, in no place, nowhere that could be recognized as somewhere. Even at 10 years old, I viscerally felt the truth onto which my teacher had stumbled.
I knew I was “Indian,” a transplanted Bengali. I had an Indian passport. I ate regionally specific Indian food, like the fish curry Bengalis called “macher jhol” and, on weekends, “luchi and begun bhaja,” fried puffy flatbread and aubergine slices. My father was one of the founders of the Bengali Cultural Society, an outlet for Bengalis in Kuwait to put on plays, sing songs and make their children recite the nonsense verse of Sukumar Ray. It gave them a space to assert their identities and retain their connections to what Indians like to call their “native place.”
My parents had no difficulty filling the blank canvas that was Kuwait with the colors of the culture they left behind. What could be easier in Kuwait than pretending you had never left India? Your social life revolved not just around other Indians but mostly around Indians just like you, in terms not just of ethnicity, region, religion and language but class, education, even profession. Kuwait dented none of their cultural confidence. Their leisure time was filled with the Bengali language and Bengali food.
For me, though, Kuwait was quite literally no place. Children like me were not like the children of immigrants to the U.S., U.K., Australia and so on — children torn between cultures, negotiating a fraught terrain between the domestic experience and the world outside. We were instead bereft of culture. Bereft of cultural context.
My claim on India was almost as tenuous as my claim to Britain. And the unstated policy of the country in which I lived was to deliberately keep at arm’s length a population of expatriate workers that outnumbered citizens. With its broad boulevards and American fast-food restaurants with cheery signage, Kuwait looked and sometimes felt like an international airport.

The Iraqi invasion had little effect on my self-absorption. I felt no fear, no swell of sympathy for my few Kuwaiti friends, mostly teammates on the school football team, all of whom were still on their summer holidays in luxury hotels and yachts across Europe. I thrilled instead to the novelty of the invasion and the promise that the school term might not begin as scheduled. The early days of the occupation passed slowly. For news, we were reliant on the elusive shortwave signal for the BBC World Service.
The only Kuwaiti we really talked to was Asrar Al-Qabandi, a young woman my mother knew who had been educated largely in the United States. Asrar was different from other Kuwaiti women. My mother had met and befriended her when she applied for a job at the playschool my mother ran. Asrar kept her hair short and usually wore baggy trousers. Her incorrigible habit of expressing her opinion made her unpopular with her family and a frequent visitor to our apartment.
Asrar used to complain to my mother about Kuwait, the country’s conservatism, the easy money that had made its people lazy and insipid, their lack of interest in education and their prejudices. She seemed to have few friends apart from my mother. Until the invasion, I had never heard her express any affection for Kuwait. I imagined Kuwait as a scab on her knee, irritating and unsightly but comforting to pick at.
Occasionally, the invasion would make its presence felt. We heard our parents talk anxiously about a close friend, a man with a pendulous belly and spry wit, who had been arrested in Iraq for carrying counterfeit dollars. Our parents panicked about their own dollars. These were bought at five times the usual rate and were the only currency Iraqis would accept in exchange for a plane ticket to Jordan, the only country that had kept its border with Iraq open.
Our encounters with the occupying soldiers were infrequent and sometimes farcical. As Indians, we were relatively safe in occupied Kuwait. We were of no interest to Iraqi soldiers, unlike Westerners who made valuable hostages and, for obvious reasons, Kuwaitis, small bands of whom, Asrar among them, were organizing and mounting a sporadic, flickering resistance. The stories told about Iraqi soldiers among Indians were mostly of buffoonery, tales tinged with condescension for soldiers stealing computer monitors they thought were TVs, for soldiers who were not Iraqi at all but bewildered Bangladeshi gardeners or Filipino drivers forced into the army as casualties in the eight-year war with Iran mounted. It was only after we left Kuwait that I read about the rapes and torture that happened during the occupation.

In the opening pages of “The Satanic Verses,” as Gibreel Farishta and Saladin Chamcha plunge towards “Proper London, capital of Vilayet,” Salman Rushdie puts the words of a famous song into Gibreel’s mouth:
O, my shoes are Japanese
These trousers English, if you please
On my head, red Russian hat
My heart’s Indian for all that
For an Indian living in India, the song is about pride, jauntily nationalistic lyrics written for a newly created nation. In contemporary India, the song is relevant and resonant as a simultaneous embrace and rejection of globalization — some things, your heart and soul, are forever local. For the immigrant Indian, the song is a defiant but futile resistance. For the Gulf-based Indian, the song is matter of fact, an accurate expression of the expat life. Of course, your heart is Indian, whatever the imported fripperies of your new, materially comfortable life. What other choice is there?
But for the Indian expat’s child, the child put into a British or American school to suit their parents’ aspirational, upwardly mobile sense of themselves, the song seemed foolish, sentimental.
How do you keep your heart free from the influence of your shoes, trousers and hat? What does it mean to have an Indian soul? For me, the idea of an authentic self was muddied, perplexing. If you come from somewhere, a particular place, and you live there all your life, an authentic self that grows organically from your sense of place is something you take for granted, so strong and defining a part of who you are that it’s hard to imagine what could diminish that land-based identity.
For us, those cosseted children of Utopia, of no place, what could fill the place-shaped hole in our identity? It’s not that the question of where you come from becomes hard to answer, it’s that it no longer has any meaning. This is distinct from the struggle of the immigrant’s child to negotiate between the place to which they now belong and their “place of origin” so inadequately represented by the short, rickety bridge of the hyphen — Vietnamese-American, say, or Afro-Caribbean British. Or from the immigrant’s division between the place remembered and the place in which you found yourself.
Part of my love for English football was for its unabashed tribalism. I remember being in my neighborhood bookshop and coming across a copy of E.P. Thompson’s canonical text “The Making of the English Working Class” and begging my bemused father to buy it. I was too young to make any sense of what I was reading but I was powerfully drawn to the idea that an entire class of people could be “made,” as if you could pull a community whole from a kiln, as if a shapeless, shifting mass of individuals could be given contours, shape and coherence.

We left Kuwait in the last week of September 1990.
My father and some of the other men staying with us had arranged for a bus and a driver to take us to the southern Iraqi city of Basra and then on to Baghdad. At dawn, we arrived in the Iraqi capital, where we stayed at a hotel for a week before we were able to board a flight to the Jordanian capital Amman.
Bengalis are, of course, India’s doughtiest tourists. For that week in Baghdad we reverted to type, eating fish and chips on the banks of the Tigris, riding the creaky rollercoaster at the empty but functioning amusement park and visiting the National Museum. Reality, the reality in which we were refugees fleeing from Kuwait, a country occupied by Iraq, the international pariah in which we were now vacationing, only occasionally intruded — in the form of empty supermarket shelves and a tour guide who begged us for our cartons of chocolate milk for her baby because the powdered variety was all that was available in Iraq.
In Amman, we slept at the airport for one night before we were able to board one of the many free flights Air India had organized to transport Indian refugees to Bombay and safety. Two months after Iraq invaded Kuwait, we were on a plane to India. I didn’t know then, still arguing with my friends about the relative merits of Liverpool and Manchester United, AC/DC and Iron Maiden, how lucky we were.
Smothered by relatives in Bombay, in my grandmother’s apartment bursting with books, art and furniture accrued over the course of entire lives of entire generations, I began to realize how ephemeral my life in Kuwait was, how thin my connection was to that place, or this place, or any place outside my own head. I was fascinated by Bombay, by its noxious drains, its rusting red double-decker buses, its panoply of streets. But I knew I didn’t belong in the city like my mother did.
Being a perpetual migrant might have been new in 1990. Today it is unremarkable. By 2020, some 280 million people around the world were estimated to be international migrants.
In “Identity and Violence,” the Nobel-winning economist Amartya Sen makes a forceful argument for the essential heterogeneity of identity, the value of each of the many parts that constitute the whole:
“The same person can be, without any contradiction, an American citizen, of Caribbean origin, with African ancestry, a Christian, a liberal, a woman, a vegetarian, a long-distance runner, a historian, a schoolteacher, a novelist, a feminist, a heterosexual, a believer in gay and lesbian rights, a theatre lover, an environmental activist, a tennis fan, a jazz musician, and someone who is deeply committed to the view that there are intelligent beings in outer space with whom it is extremely urgent to talk (preferably in English).”
Wonderful as this passage is, my response is an impatient “yes, but…” The global response to such blithe cosmopolitanism has been the parochialism espoused by the likes of Narendra Modi, Donald Trump and recently elected right-wing governments in countries like Italy and Sweden. Months after Britain voted in 2016 to leave the European Union, then-Prime Minister Theresa May told a Conservative Party conference that if “you believe you are a citizen of the world, you are a citizen of nowhere.”
I know what she means. I am a middle-aged Indian man. I have an Indian wife and two Indian children. We live in India. My wife and I are both Bengali and, though neither of us is even slightly religious, our surnames place us safely among the Hindu upper castes that control India.
Protected by these markers of “Indianness,” my place in Indian society is unquestioned, even as Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi does the bidding of his ideological masters and remakes India from a pluralistic, secular nation into an increasingly belligerent, nostalgia-fueled Hindu nation. This state that makes life so difficult for the poor, the disenfranchised, the lower caste and the Muslim looks upon us with benevolence and avuncular affection.
It’s discomfiting to have spent so much time feeling out of place, only to find that it is the external, most superficial markers of my identity that both define and legitimize me in Modi’s new India.
All I have to do is keep my mouth shut, lest I give myself away.

Ensconced in India, ostensibly an unimpeachable citizen of somewhere, I remain indelibly marked by my years in “no place.” I have spent most of my life in cities to which I have no claim other than temporary residence. My perspective has been that of the perpetual, if privileged, outsider. It’s a common enough modern condition but, as former Prime Minister May argued, still suspect.
In a speech in 1993 — ironically in defense of greater integration with Europe — another former British prime minister, John Major, offered a lyrical, classically rural vision of “timeless” Britain. “Fifty years from now,” he said, “Britain will still be the country of long shadows on county grounds, warm beer, invincible green suburbs, dog lovers… Britain will survive unamendable in all essentials.”
Similarly, the real India, we are always told, is to be found in its villages. Indeed, only 35% of Indians live in cities. And in many of those cities we retain a parochial suspicion and fear of outsiders, of behavior that we consider strange and do not recognize as our own. Just a few years ago, for the first time in its long history, China became a predominantly urban society, with over 50% of its people living in cities. The 2009 documentary, “Last Train Home,” showed the toll of urbanization on one poor Chinese couple who work in a factory, cut off from their village, their growing daughter, their values and everything they’ve ever known or taken for granted. The annual trip home only emphasizes their alienation.
Yet their daughter, despite her parents’ unhappiness, abandons her own education to seek work in the city, drawn by that same desire for independence, for freedom from the social bonds of village life. India is headed in this direction.
Global cities remain vast agglomerations of outsiders. It is partly why these monstrous conurbations are so reviled. Back in 1987, Hanif Kureishi offered a stirring defense of London in “Sammy and Rosie Get Laid,” the movie he wrote, directed by Stephen Frears. Sammy’s father, a compromised Pakistani politician, points out that London is a “cesspit.”
What can Sammy possibly like about this city? London is beset by race riots, poverty, violence and crime. “Well,” Sammy tells his father, “on Saturdays, we like to walk on the Towpath and kiss and argue.” It’s the beginning of a short disquisition on metropolitan pleasures. “Neither of us is English,” he says of himself and Rosie, “we’re Londoners, you see.”
Community feeling can emerge even within collections of outsiders. Kureishi’s London in the 1980s — resistant to authority, carnivalesque, an ad hoc and mutable community of outsiders — is distinct from the country around it. Major’s Britain is inimical to Kureishi’s London: one “unamendable” where the other is protean, one a sun-dappled, bucolic idyll where the other is unrestrainedly rough and urban, one faithful to what has been before where the other craves the new, the mixed, the composite culture of a city marked by migratory flows.

Shortly before the Allies began Operation Desert Storm on January 17, 1991, I began my first semester at a boarding school in the Palani Hills in Kerala. In the library at my new school, I discovered in an issue of TIME magazine that my mother’s old friend Asrar had been arrested by the Iraqis. She had been shot, I read in one account, seven times in each breast and seven times in the vagina. In another, I read she had been shot four times in the head, once between the eyes, and that the right side of her face had been cut open with an ax. The accounts of the work she did for the Kuwaiti resistance — running guns and money from Saudi Arabia, destroying Iraqi communications systems, disguising herself as a cleaner to smuggle out vital records and documents from ministries now guarded by dozens of occupying soldiers — are impossible to reconcile with the small, bespectacled woman I remember. But even back then her size belied her spirit.

Asrar was hailed in death by her family as she had never been in life, hailed as a martyr for the cause of a country she had little regard for until it was taken away. I thought of Asrar in 2019, when young people in Delhi began protesting the Modi government’s exclusive, narrow, parochial view of Indian citizenship as expressed in the Citizenship Amendment Act. Before the pandemic forced them off the streets, the protestors, many of whom would have been unaffected by amendments aimed at Muslims and minorities, were fighting for an idea of India. An India forged in the constitutional ideals of plurality and democracy. They were saying, “We are not a Hindu nation.” We will not be refashioned into a theocratic state built on principles of exclusion and prejudice. Perhaps, like Asrar, these young people were motivated to fight for an India they saw was being taken away from them, to fight for the secular ideals with which they had grown up, whatever the failings of the state to live up to those ideals.
In Modi’s new India, words such as “secular” and “plural” were to be jettisoned as the follies of governments past. But the protests did not reflect the smug cosmopolitanism of an elite diaspora or a cosmopolitanism that offered no challenge to the prevailing order. Instead, it struck me as a revivifying commitment to community as a cobbled-together, living thing that expands rather than contracts.
It showed me a path forward, out of a complacent, calcified nostalgia for my utopian “no place.” What I thought I missed growing up in Kuwait was community. In my hermetically sealed room, in my imagination unsoured, uninflected by experience, I tried to understand what it was to be a part of something larger than yourself, to belong somewhere and to claim it as your own.
The wrongheaded answer I came up with was to fetishize the local, to fetishize community as a club from which I was excluded when — to borrow from Woody Allen borrowing from Groucho Marx — I would never want to belong to a club that would have someone like me for a member.
What I didn’t know was that communities cannot be so easily confined, so neatly shaped. That outsiders, too, can form communities. That outsiders, too, can find their place.